Abstract
Background
The REACH3 study has reported greater overall response and failure-free survival (FFS) with Ruxolitinib (RUX) as 2 nd line therapy for steroid-refractory chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) in comparison to best available therapy (BAT; NEJM 2021). In addition, our Canadian retrospective study as a real-world experience has reported a promising activity of 64.6% FFS and 83.3% overall survival (OS) at 12 months in 115 patients (pts) treated with RUX from 2016 to 2021 for heavily pretreated cGVHD (ASH 2021). Also, 47.6% pts could reduce corticosteroid dose below 0.1mg/kg/day within 6 months.
The present study compared treatment outcomes using a propensity-score matching (PSM) analysis between RUX pts ("RUX group", n=115) and a historical cohort of cGVHD pts treated with BAT as 2 nd line therapy or beyond from 2005 to 2013 ("BAT group", n=311). Statistical endpoints such as FFS, OS and steroid dose reduction were evaluated instead of overall response due to limited response assessment available from retrospective chart reviews.
Patients and methods
BAT included mycophenolate (43%), prednisone (29%), prednisone/cyclosporine (12%), extracorporeal photopheresis (6%), rituximab (3%), and others (7%). The pts and disease characteristics between the RUX vs BAT groups were not well balanced, as expected: RUX group showed a higher number of pts with severe grade GVHD (59.1% in RUX vs. 20.3% in BAT; p<0.0001), and more heavily pretreated with 4 th line or beyond (84.3% in RUX vs. 17.0% in BAT; p<0.0001).
FFS and OS were calculated from the day of starting RUX or BAT therapy, while daily prednisone doses at months 0, 3 and 6 were calculated divided by body weight (kg). PSM analysis was applied to adjust risk factors that were unbalanced between the 2 groups, including GVHD severity at therapy start (mild/moderate vs severe grade), HCT-CI score (0-2 vs 3 or beyond), and treatment line (2nd vs 3rd vs 4th line or beyond). A total of 100 patients (i.e. 50 case-control pairs) were finally extracted through PSM process within 0.2 of calliper difference. PSM analysis balanced out the risk factors between the 2 groups: GVHD severity (p=1.0), HCT-CI score (p=1.0) and treatment line (p=1.0). The FFS and OS rate at 12 months were compared using Cox's proportional hazard model.
Results
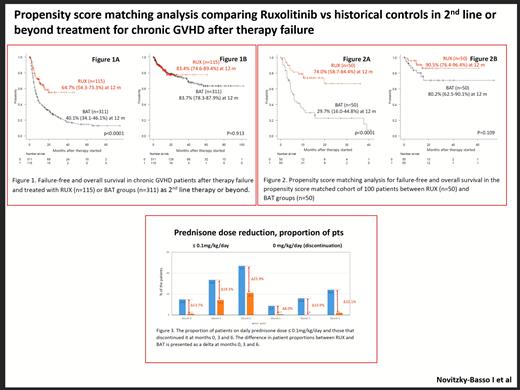
In the overall population (n=426), with a median 19 months follow-up duration, 244 failures (57.3%) were noted. While both groups showed similar failure rates due to non-relapse mortality (NRM), the RUX group showed significantly lower failure rate from cGvHD resistance requiring therapy switch. Failure was noted in 40 pts (33.4%) in RUX due to resistance requiring a switch of therapy (n=23; 20.0%), NRM (n=14, 12.2%) and relapse (n=3; 2.6%), while failure occurred in 204 pts (65.6%) in BAT due to resistance requiring a switch of therapy (n=142; 45.7%), NRM (n=36; 11.6%) and relapse (n=26; 12.7%).
The 12 months' FFS rate were 64.7% and 40.1% in RUX vs. BAT group (p<0.0001; Fig 1A), while the 12 months' OS rate were 83.4% and 83.7% in RUX vs. BAT group (p=0.913; Fig 1B). In the propensity score matched (PSM) cohort (n=100), the RUX group showed a survival benefit over the BAT group: the 12 months' FFS rate was 74.0% and 29.7% in RUX vs. BAT group (p<0.0001; Fig 2A), while the 12 months' OS rate were 90.5% and 80.2% in RUX vs. BAT group (p=0.109; Fig 2B).
Multivariate analysis in the PSM cohort confirmed that RUX is superior to BAT for FFS (p<0.001, HR 0.267 [0.139-0.516]) together with HCT-CI score 0-2 vs ≥3 (p=0.037, HR 0.490 [0.251-0.959]) with a trend to better survival in RUX over BAT (p=0.110, HR 0.402 [0.131-1.228]).
The prednisone dose was gradually reduced over time: the median doses of prednisone at months 0, 3, and 6 were 0.34, 0.16 and 0.02 mg/kg/day in the RUX group, and 0.95, 0.24 and 0.15 mg/kg/day at months 0, 3 and 6 in the BAT group.
RUX facilitates the discontinuation of prednisone. The proportions of patients who discontinued prednisone at months 0, 3 and 6 were 8.7%, 15.9% and 24.1% in RUX, and 0.7%, 0% and 2.0% in BAT group. The differences in proportions of pts that discontinued prednisone between the RUX vs BAT groups at months 0, 3, and 6 were 8.0%, 15.9% and 22.1% (Fig 3).
Conclusion:
The current PSM analysis study suggests that RUX showed a superior FFS to BAT as 2nd line therapy or beyond in cGVHD patients after therapy failure. RUX showed better steroid tapering compared to BAT.
White: Novartis: Honoraria. Elemary: Pfizer, Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz, BMS, Abbvie, Novartis, Pfiz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hamad: Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Law: Novartis: Consultancy; Actinium Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Kim: Bristol-Meier Squibb: Research Funding; Paladin: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal